Portal Azure: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know in 2024
Welcome to the ultimate guide on Portal Azure — your gateway to managing cloud resources with ease, efficiency, and enterprise-grade control. Whether you’re a developer, IT admin, or cloud architect, mastering this platform is non-negotiable in today’s digital landscape.
What Is Portal Azure and Why It Matters

Portal Azure, officially known as the Azure Portal, is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing its vast ecosystem of cloud services. Think of it as the central command center for everything Azure — from virtual machines and databases to AI tools and security policies.
The Evolution of Cloud Management Interfaces
Before the rise of intuitive dashboards like Portal Azure, managing cloud infrastructure was a command-line-heavy task, often requiring deep technical knowledge and scripting expertise. The introduction of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) revolutionized how teams interact with cloud platforms.
- Early cloud management relied on CLI (Command Line Interface) tools.
- GUIs like Portal Azure democratized access, enabling non-developers to manage resources.
- Today’s portals integrate AI-driven insights, cost analytics, and real-time monitoring.
Core Purpose and Target Users
Portal Azure serves multiple roles depending on the user. For developers, it’s a sandbox for deploying apps. For DevOps engineers, it’s a hub for automation and CI/CD pipelines. For business leaders, it offers visibility into spending and performance.
- Developers: Deploy, test, and monitor applications.
- IT Administrators: Manage access, security, and network configurations.
- Finance Teams: Track usage, set budgets, and optimize costs.
“The Azure Portal isn’t just a tool — it’s the nerve center of your cloud operations.” — Microsoft Cloud Documentation
Key Features That Make Portal Azure Stand Out
Portal Azure isn’t just another dashboard. It’s packed with powerful features designed to simplify complex tasks, enhance visibility, and accelerate deployment cycles. Let’s dive into what makes it indispensable.
Unified Dashboard and Resource Management
One of the most praised aspects of Portal Azure is its unified dashboard. From a single screen, users can view all their resources — whether they’re virtual machines, storage accounts, or Kubernetes clusters.
- Customizable tiles for quick access to frequently used services.
- Drag-and-drop functionality to organize the dashboard layout.
- Real-time status updates across all connected regions and subscriptions.
This level of integration reduces context switching and improves operational efficiency. According to Microsoft’s official documentation, over 90% of Azure users rely on the portal for daily management tasks.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
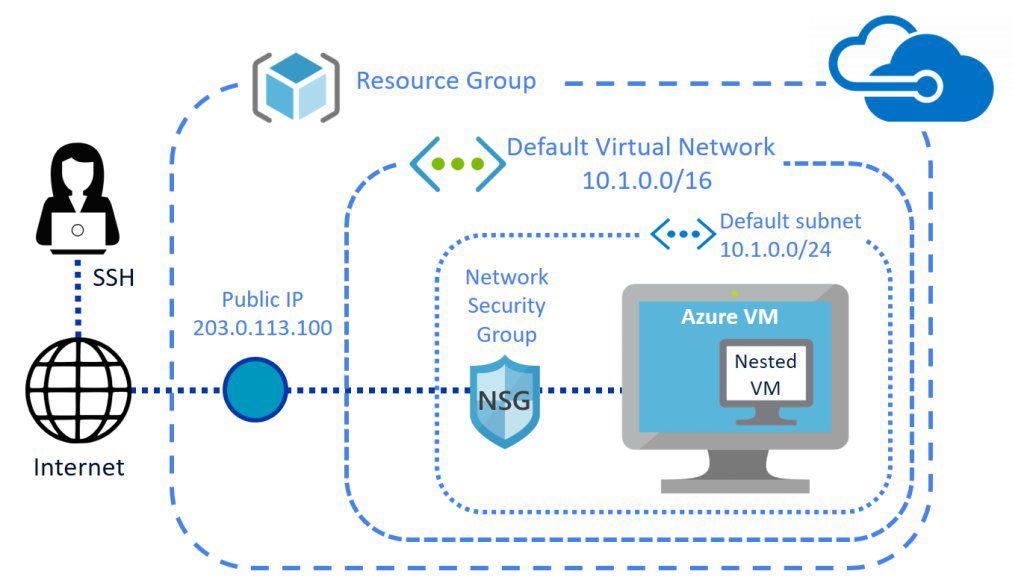
Security is paramount in cloud environments, and Portal Azure delivers robust Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). This feature allows administrators to assign granular permissions based on job functions.
- Predefined roles like Owner, Contributor, and Reader.
- Custom roles for specialized access needs.
- Integration with Azure Active Directory (AAD) for identity management.
For example, a database administrator might have full access to SQL databases but no权限 to modify virtual networks. This principle of least privilege enhances security and compliance.
Monitoring and Diagnostics with Azure Monitor
Portal Azure integrates seamlessly with Azure Monitor, providing real-time insights into application health, performance metrics, and log data.
- Live metrics streams for CPU, memory, and disk usage.
- Custom alerts based on thresholds (e.g., high latency or failed requests).
- Log Analytics workspace for deep troubleshooting.
With Azure Monitor embedded directly into the Portal Azure interface, teams can detect issues before they impact end-users, reducing downtime and improving service reliability.
How to Get Started with Portal Azure
Getting started with Portal Azure is straightforward, even for beginners. Whether you’re setting up your first subscription or managing a multi-tenant environment, the onboarding process is designed to be intuitive.
Creating an Azure Account and Subscription
The first step is signing up for an Azure account. Microsoft offers a free tier that includes $200 in credits for new users, valid for 30 days, plus access to over 25 always-free services.
- Visit azure.microsoft.com/free to sign up.
- Use a personal email or work account linked to Microsoft.
- Verify identity via phone or credit card (no charges for free tier).
Once registered, you’ll create a subscription — essentially a billing container for your resources. You can have multiple subscriptions under one account, ideal for separating development, testing, and production environments.
Navigating the Portal Azure Interface
After logging in, you’ll land on the default dashboard. Here’s a quick tour of the key components:
- Navigation Menu (Left Sidebar): Access services like Virtual Machines, Storage, and AI.
- Search Bar: Instantly find any service or setting.
- Resource Groups: Logical containers for organizing related resources.
- Quickstart Center: Guided tutorials for common tasks.
Familiarizing yourself with these elements early on will save time and reduce errors when scaling your cloud operations.
Deploying Your First Resource
Let’s walk through deploying a simple virtual machine (VM) using Portal Azure:
- Click Create a resource in the top-left corner.
- Search for “Virtual Machine” and select it.
- Choose a subscription and create a new resource group (e.g.,
my-first-rg). - Select a region (e.g., East US).
- Pick a VM image (Windows or Linux).
- Configure size, authentication, and networking.
- Click Review + Create, then Create.
In minutes, your VM will be provisioned and ready to use. This simplicity is one of the reasons why Portal Azure has become the go-to interface for cloud beginners and experts alike.
Advanced Tools and Integrations in Portal Azure
While basic resource management is valuable, Portal Azure truly shines when leveraging its advanced tools and integrations. These capabilities empower teams to automate workflows, enforce policies, and maintain compliance at scale.
Azure Policy and Governance
As organizations grow, so does the risk of misconfigurations and policy violations. Portal Azure includes Azure Policy, a service that enforces organizational standards and assesses compliance.
- Define rules such as “Only approved VM SKUs are allowed.”
- Automatically audit existing resources for compliance.
- Remediate non-compliant resources with built-in actions.
For example, a company might use Azure Policy to ensure all storage accounts are encrypted at rest, preventing data breaches due to oversight.
Automation with Azure Logic Apps and Runbooks
Repetitive tasks eat up valuable time. Portal Azure supports automation through tools like Azure Logic Apps and Automation Accounts with PowerShell runbooks.
- Logic Apps enable no-code workflows (e.g., send email on alert).
- Runbooks allow scheduled scripts to start/stop VMs during off-hours.
- Integrate with third-party apps like Slack, Teams, or Salesforce.
These automations not only reduce manual effort but also improve consistency and reduce human error.
Integration with DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
Portal Azure plays a critical role in modern DevOps practices. Through integration with Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and Terraform, developers can deploy code directly from repositories.
- Create deployment pipelines with visual editors.
- Use ARM templates or Bicep files for infrastructure-as-code (IaC).
- Monitor deployments in real time with logs and traces.
This tight integration between Portal Azure and development workflows accelerates release cycles and improves collaboration between teams.
Security and Compliance in Portal Azure
In an era of increasing cyber threats and regulatory demands, security cannot be an afterthought. Portal Azure provides a comprehensive suite of tools to protect data, identities, and infrastructure.
Azure Security Center and Defender
Microsoft Defender for Cloud (formerly Azure Security Center) is a unified security management and advanced threat protection service accessible directly from Portal Azure.
- Continuous assessment of security posture.
- Threat detection using AI and behavioral analytics.
- Recommendations for hardening resources (e.g., enabling MFA).
It supports hybrid environments, meaning you can monitor on-premises servers alongside cloud workloads — a major advantage for enterprises in transition.
Data Encryption and Identity Management
Portal Azure ensures data protection both in transit and at rest:
- All data moving between clients and Azure is encrypted with TLS.
- At-rest encryption uses AES-256 by default for storage services.
- Customers can manage keys via Azure Key Vault for greater control.
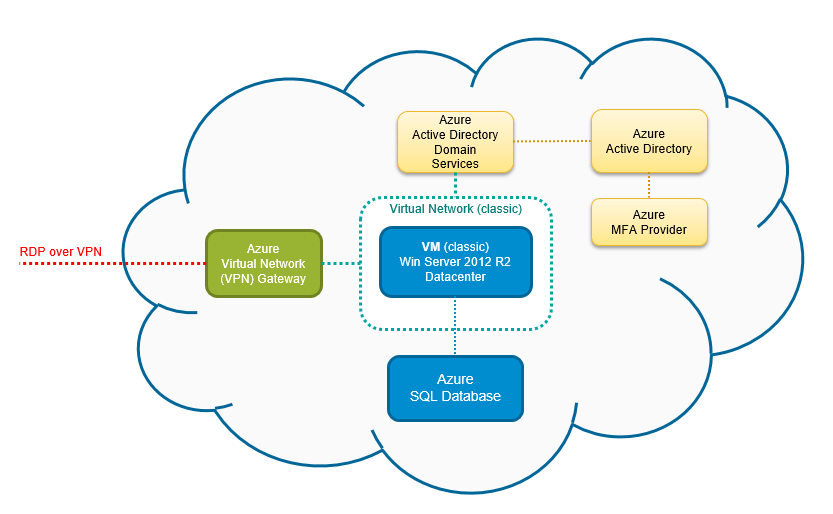
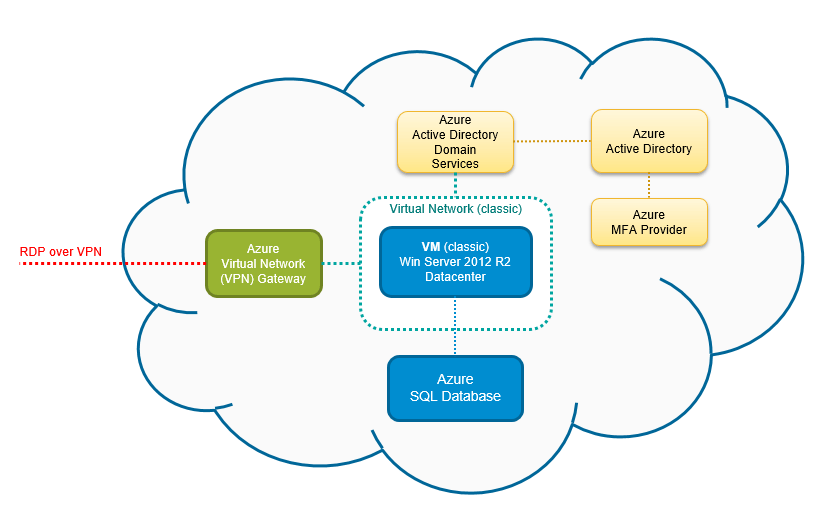
For identity, Azure Active Directory (AAD) integrates natively with Portal Azure, supporting Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), conditional access policies, and single sign-on (SSO) across thousands of SaaS apps.
Compliance and Audit Logging
Organizations in regulated industries (finance, healthcare, government) benefit from Portal Azure’s extensive compliance certifications.
- Certified for GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, SOC 1/2, and more.
- Azure Blueprints help enforce compliance templates.
- Azure Activity Log tracks every action taken in the portal for audit purposes.
These features make it easier to pass audits and demonstrate due diligence in data governance.
Cost Management and Optimization via Portal Azure
One of the biggest challenges in cloud computing is controlling costs. Without proper oversight, cloud bills can spiral out of control. Portal Azure includes powerful cost management tools to help organizations stay within budget.
Understanding Azure Pricing Models
Azure offers several pricing models, and understanding them is key to optimization:
- Pay-as-you-go: Pay only for what you use (ideal for variable workloads).
- Reserved Instances: Commit to 1- or 3-year terms for up to 72% savings.
- Spot VMs: Use unused capacity at steep discounts (up to 90%) for fault-tolerant workloads.
Portal Azure provides a pricing calculator and total cost of ownership (TCO) tool to estimate expenses before deployment.
Using Azure Cost Management + Billing
This built-in tool gives detailed insights into spending patterns:
- Visual dashboards showing daily, weekly, and monthly costs.
- Breakdown by service, resource group, or department.
- Budget alerts when spending exceeds thresholds.
You can export reports to CSV or integrate with Power BI for deeper analysis. For example, a company might discover that idle VMs are consuming 30% of their budget — an easy fix with auto-shutdown policies.
Right-Sizing and Resource Tagging
Two best practices for cost control are right-sizing and tagging:
- Right-sizing: Match VM sizes to actual workload needs (e.g., downsize from D8 to D4 if CPU usage is low).
- Tagging: Apply metadata like “Environment=Production” or “Owner=Marketing” to track ownership and allocate costs accurately.
Portal Azure makes it easy to apply tags during resource creation and filter views by tag, improving accountability and financial transparency.
Best Practices for Maximizing Portal Azure Efficiency
To get the most out of Portal Azure, it’s essential to follow proven best practices. These strategies improve performance, security, and long-term maintainability.
Organize with Resource Groups and Tags
Always group related resources (e.g., web server, database, cache) into a single resource group. This simplifies management, backup, and deletion.
- Name resource groups clearly (e.g.,
rg-prod-web-eus). - Use tags for cost allocation, environment type, and project ownership.
- Avoid placing unrelated resources in the same group.
Leverage Templates for Consistency
Instead of manually creating resources, use Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates or Bicep files to define infrastructure as code.
- Ensure consistent deployments across environments.
- Version-control your infrastructure like application code.
- Deploy with a single click from the Portal Azure interface.
This approach eliminates configuration drift and supports DevOps automation.
Enable Monitoring and Alerts Proactively
Don’t wait for an outage to set up monitoring. Configure alerts early for critical metrics:
- High CPU or memory usage.
- Failed login attempts.
- Service health advisories.
Use Action Groups to notify teams via email, SMS, or webhook integrations (e.g., to Slack or PagerDuty).
Future Trends and Innovations in Portal Azure
Portal Azure is not static — Microsoft continuously enhances it with AI, improved UX, and deeper integrations. Staying ahead of these trends ensures your organization remains competitive.
Azure AI Studio and Copilot Integration
Microsoft is embedding AI deeply into Portal Azure. Azure AI Studio allows developers to build, test, and deploy machine learning models directly from the portal.
- Access pre-trained models for vision, language, and speech.
- Use Azure OpenAI Service to integrate GPT models into apps.
- Future updates may include AI-powered Copilot suggestions for cost optimization or security fixes.
This shift toward AI-augmented cloud management will reduce manual effort and improve decision-making.
Enhanced Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Support
While Azure is a public cloud, many organizations operate in hybrid or multi-cloud environments. Portal Azure now supports:
- Azure Arc for managing servers and Kubernetes clusters anywhere.
- Integration with AWS and Google Cloud via APIs and partner tools.
- Unified billing and monitoring across clouds (in preview).
This flexibility ensures that Portal Azure remains relevant even in complex, distributed architectures.
Improved Accessibility and Mobile Experience
Microsoft is investing in making Portal Azure more accessible:
- Screen reader compatibility and keyboard navigation.
- High-contrast themes for visually impaired users.
- Mobile-responsive design for on-the-go management (limited functionality).
While full mobile management isn’t recommended for critical tasks, the ability to check alerts or restart a service from a phone adds convenience.
What is Portal Azure used for?
Portal Azure is used to manage Microsoft Azure cloud services through a web-based interface. It allows users to deploy, configure, monitor, and secure cloud resources like virtual machines, databases, networking, and AI tools. It’s essential for developers, IT admins, and business leaders who need centralized control over their cloud environment.
Is Portal Azure free to use?
Yes, accessing the Portal Azure interface itself is free. However, the cloud resources you create and manage through it (like VMs, storage, and databases) incur costs based on usage. Microsoft offers a free account with $200 in credits and access to free-tier services for 12 months.
How do I secure my Portal Azure account?
To secure your Portal Azure account, enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to limit permissions, monitor sign-in logs via Azure AD, and apply security policies through Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Regularly review user access and rotate credentials.
Can I manage non-Microsoft clouds from Portal Azure?
Direct management of AWS or Google Cloud resources isn’t natively supported, but Azure Arc and third-party integrations allow limited cross-cloud visibility and control. Microsoft is expanding multi-cloud capabilities, especially for hybrid environments.
What is the difference between Azure Portal and Azure CLI?
The Azure Portal is a graphical user interface (GUI) for managing Azure services, ideal for beginners and visual learners. Azure CLI is a command-line tool for scripting and automation, preferred by developers and DevOps teams for repeatable tasks. Both can be used together for maximum flexibility.
Portal Azure is far more than just a dashboard — it’s the central nervous system of your cloud infrastructure. From deploying virtual machines to enforcing enterprise-wide security policies, its capabilities are vast and continuously evolving. By mastering its features — from RBAC and cost management to AI integration and automation — organizations can unlock unprecedented efficiency, security, and innovation. Whether you’re just starting out or optimizing a mature cloud environment, Portal Azure remains an indispensable tool in the modern tech stack. The future of cloud management is here, and it’s powered by Portal Azure.
Further Reading: