Azure Kubernetes Service : 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
Welcome to the future of container orchestration in the cloud. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is Microsoft’s managed Kubernetes solution that simplifies deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications. Whether you’re a developer, DevOps engineer, or cloud architect, AKS offers a robust, secure, and highly scalable platform to run your workloads with ease.
What Is Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)?

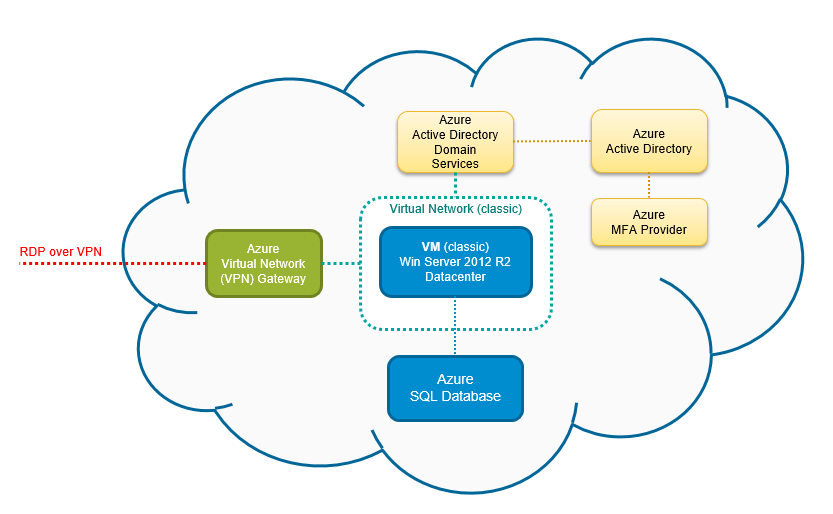
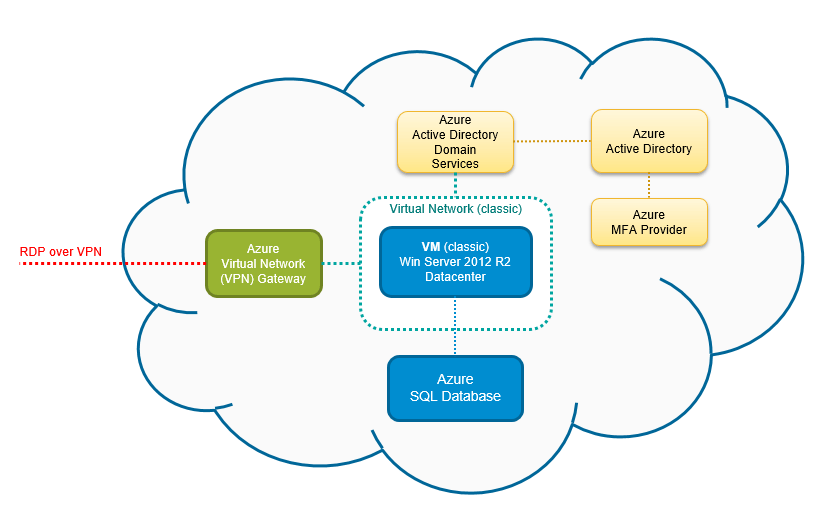
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a fully managed container orchestration platform provided by Microsoft Azure. It allows organizations to deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications using Kubernetes without the complexity of managing the underlying control plane. AKS handles critical tasks such as node provisioning, upgrades, health monitoring, and security patching, enabling developers to focus on building applications rather than infrastructure.
Core Components of AKS
Understanding the architecture of AKS is essential for leveraging its full potential. The service is built on several key components that work together to deliver a seamless Kubernetes experience.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Control Plane: Managed entirely by Azure, the control plane includes the Kubernetes API server, scheduler, and etcd.You don’t need to manage or pay for these components directly.Node Pools: These are groups of virtual machines (VMs) that run your containerized workloads.You can configure multiple node pools with different VM sizes, operating systems, and scaling policies.
.Kubelet and Container Runtime: Each node runs the kubelet agent and a container runtime (typically containerd) to communicate with the control plane and execute containers.How AKS Differs from Self-Managed Kubernetes
Running Kubernetes on your own infrastructure or using open-source tools like kubeadm requires significant operational overhead.AKS eliminates this burden by offering a managed control plane, automatic upgrades, integrated monitoring, and native Azure integrations..
“AKS reduces the complexity of Kubernetes operations by up to 70%, allowing teams to focus on innovation rather than maintenance.” – Microsoft Azure Documentation
Unlike self-managed clusters, AKS provides built-in high availability for the control plane, automatic node health checks, and seamless integration with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), Azure Monitor, and Azure Policy.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Key Features of Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) stands out due to its rich set of features designed to enhance developer productivity, security, and scalability. These features make AKS one of the most popular managed Kubernetes services in the enterprise space.
Automated Kubernetes Management
One of the biggest advantages of AKS is its automation capabilities. Azure automatically manages the Kubernetes control plane, including:
- Automatic patching and updates
- Control plane high availability across multiple availability zones
- Auto-healing of failed control plane components
This means you can deploy clusters in minutes and keep them up-to-date with minimal effort. For example, upgrading your Kubernetes version can be done with a single CLI command or via the Azure portal.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Integrated Security and Identity
Security is a top priority in AKS. The service integrates deeply with Azure’s identity and access management ecosystem:
- Azure AD Integration: Enables role-based access control (RBAC) using corporate identities, making it easier to manage user permissions.
- Managed Identities: Eliminates the need to manage service principal credentials by using Azure-managed identities for resource access.
- Network Policies: Enforce pod-to-pod communication rules using Calico or Azure Network Policies.
Additionally, AKS supports integration with Azure Key Vault for secure storage of secrets and certificates.
Scalability and Performance Optimization
AKS offers multiple layers of scalability to meet dynamic workload demands:
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Cluster Autoscaler: Automatically adjusts the number of nodes based on resource demand.
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA): Scales the number of pod replicas based on CPU or custom metrics.
- Virtual Nodes (Azure Container Instances): Allows bursting workloads into serverless containers for rapid scaling without provisioning VMs.
These features ensure your applications remain responsive during traffic spikes while optimizing cost efficiency.
Setting Up Your First Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) Cluster
Getting started with Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is straightforward, whether you prefer the Azure portal, CLI, or infrastructure-as-code tools like Terraform or Bicep.
Prerequisites for AKS Deployment
Before creating an AKS cluster, ensure you have the following:
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- An active Azure subscription
- Azure CLI installed (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli)
- Basic understanding of Kubernetes concepts (pods, services, deployments)
- Resource Group to organize your cloud resources
You can also use Azure Cloud Shell, which comes pre-installed with the Azure CLI and kubectl, the Kubernetes command-line tool.
Step-by-Step Cluster Creation Using Azure CLI
Here’s how to create a basic AKS cluster using the Azure CLI:
- Login to Azure:
az login - Create a resource group:
az group create --name myResourceGroup --location eastus - Create the AKS cluster:
az aks create --resource-group myResourceGroup --name myAKSCluster --node-count 2 --enable-addons monitoring --generate-ssh-keys - Install kubectl:
az aks install-cli - Connect to the cluster:
az aks get-credentials --resource-group myResourceGroup --name myAKSCluster - Verify connection:
kubectl get nodes
This will deploy a two-node cluster with Azure Monitor enabled for logging and performance insights.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Deploying Your First Application on AKS
Once your cluster is up and running, you can deploy a sample application. For example, deploy an Nginx web server:
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx
kubectl expose deployment nginx --type=LoadBalancer --port=80After a few minutes, run kubectl get services to retrieve the public IP address. You’ll see your Nginx server accessible over the internet.
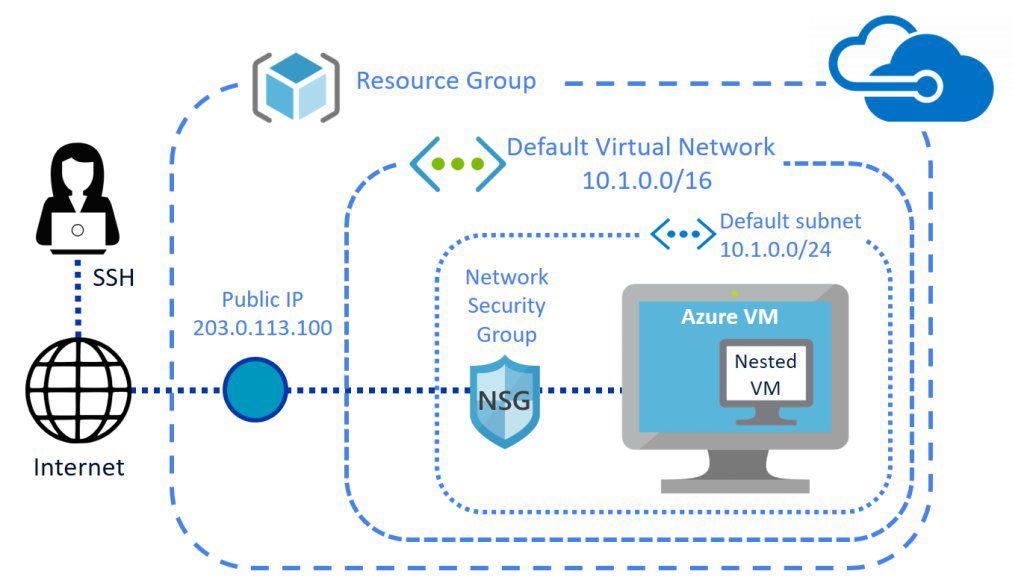
Networking in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Networking is a critical aspect of any Kubernetes deployment. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) provides flexible and secure networking options to support various deployment patterns and compliance requirements.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Understanding AKS Networking Models
AKS supports two primary networking models:
- kubenet: A basic networking model where Azure handles IP address assignment. Suitable for simple deployments but limited in scalability and policy enforcement.
- Azure CNI (Container Networking Interface): Assigns each pod an IP address from the virtual network subnet, enabling direct communication with other Azure resources. Ideal for hybrid connectivity and advanced network policies.
Choosing the right model depends on your scalability needs, security policies, and integration requirements with existing VNet architectures.
Configuring Ingress and Load Balancing
To expose your applications securely, AKS supports multiple ingress patterns:
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Azure Load Balancer: Provides Layer 4 (TCP/UDP) load balancing for direct external access.
- Application Gateway Ingress Controller (AGIC): Enables Layer 7 (HTTP/HTTPS) routing with SSL termination, URL-based routing, and WAF integration.
- NGINX Ingress Controller: Popular open-source option for custom routing rules and middleware support.
You can deploy AGIC using Helm charts or via the Azure portal, integrating it seamlessly with existing App Gateway instances.
Securing Network Traffic with Azure Firewall and NSGs
For enterprise-grade security, AKS integrates with Azure Firewall and Network Security Groups (NSGs) to control inbound and outbound traffic:
- Use NSGs to restrict traffic between subnets and services.
- Deploy Azure Firewall for centralized egress filtering, threat intelligence, and FQDN-based rules.
- Enable private clusters to hide the API server behind a private endpoint, reducing exposure to the public internet.
These capabilities are essential for meeting regulatory standards like HIPAA, GDPR, or SOC 2.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Security Best Practices for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
While AKS provides strong security out of the box, following best practices ensures your clusters remain resilient against threats and misconfigurations.
Enable Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC allows fine-grained control over who can perform actions within your cluster. Always define roles and role bindings based on the principle of least privilege:
- Use Azure AD groups to map users to Kubernetes roles.
- Avoid using cluster-admin unless absolutely necessary.
- Leverage Azure Policy for Kubernetes to enforce RBAC policies at scale.
For example, you can restrict developers to only view or manage resources in specific namespaces.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Use Pod Security Policies (or Azure Policy for Kubernetes)
Pod Security Policies (PSPs) were deprecated in Kubernetes 1.25, but AKS supports their replacement through Azure Policy for Kubernetes. This service allows you to enforce policies such as:
- Preventing privileged containers
- Requiring read-only root filesystems
- Blocking containers running as root
You can audit or block non-compliant deployments, ensuring consistent security posture across all clusters.
Enable Logging, Monitoring, and Threat Detection
Visibility is key to detecting anomalies and responding to incidents. AKS integrates with:
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Azure Monitor for Containers: Provides real-time performance metrics, logs, and alerts.
- Microsoft Defender for Containers: Offers vulnerability scanning, runtime threat detection, and compliance monitoring.
- Azure Sentinel: Enables SIEM integration for advanced threat hunting and incident response.
Enable these services early in your deployment lifecycle to gain continuous insight into cluster health and security.
Scaling and Cost Optimization in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Efficient scaling and cost management are crucial for maintaining performance while controlling cloud spending. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) offers several tools and strategies to optimize both.
Auto-Scaling Strategies in AKS
AKS supports multiple auto-scaling mechanisms:
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Cluster Autoscaler: Adds or removes nodes based on pending pods. Configure it during cluster creation or enable it later.
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA): Scales the number of replicas based on CPU, memory, or custom metrics from Prometheus or Azure Monitor.
- KEDA (Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaling): Allows scaling based on external events like message queue depth or HTTP request rate.
Combining HPA with the cluster autoscaler ensures your applications scale seamlessly under load.
Using Spot Instances and Low-Priority Nodes
To reduce costs, AKS supports spot VMs (formerly low-priority VMs) for fault-tolerant workloads:
- Spot instances can save up to 90% compared to on-demand pricing.
- Ideal for batch jobs, CI/CD pipelines, or stateless microservices.
- Configure eviction policies and graceful shutdowns to minimize disruption.
You can mix spot and on-demand nodes in the same cluster using multiple node pools, balancing cost and reliability.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Cost Monitoring and Governance with Azure Cost Management
To track and optimize spending, integrate AKS with Azure Cost Management:
- Tag resources (clusters, node pools, namespaces) for chargeback and showback.
- Set budgets and alerts for unexpected spikes.
- Use Azure Advisor to get recommendations on resizing underutilized nodes.
Additionally, tools like Kubecost can be deployed on AKS to provide granular cost allocation per namespace or team.
Integrating Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) with CI/CD Pipelines
Modern software delivery relies on automated CI/CD pipelines. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) integrates seamlessly with Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and other DevOps tools to enable continuous deployment.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Setting Up CI/CD with Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps provides a complete suite for building, testing, and deploying applications to AKS:
- Create a build pipeline to containerize your app using Docker.
- Push images to Azure Container Registry (ACR).
- Configure a release pipeline using the Kubernetes manifest task to deploy to AKS.
You can also use service connections to authenticate with AKS securely using managed identities.
Using GitHub Actions for AKS Deployments
For teams using GitHub, GitHub Actions offers native support for deploying to AKS:
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Use the
azure/aks-set-contextaction to authenticate. - Deploy using
azure/k8s-deploywith Helm or Kubernetes manifests. - Leverage OpenID Connect (OIDC) for secure, token-based authentication without storing secrets.
This integration enables GitOps workflows where every merge to main triggers a deployment.
Implementing GitOps with Flux or Argo CD
GitOps is a modern approach where the desired state of your cluster is stored in Git. Tools like Flux and Argo CD can be deployed on AKS to sync cluster state with Git repositories:
- Define deployments, services, and configurations in YAML files.
- Automatically apply changes when commits are pushed.
- Enable rollback by reverting Git commits.
Microsoft also offers Microsoft Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes to extend GitOps to on-premises and multi-cloud clusters.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Advanced Use Cases and Enterprise Adoption of Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
As organizations mature in their cloud journey, they leverage Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) for complex, mission-critical workloads beyond basic container orchestration.
Running Stateful Applications on AKS
While Kubernetes is often associated with stateless apps, AKS supports stateful workloads through:
- Azure Disks and Azure Files for persistent volumes.
- Dynamic provisioning using StorageClasses.
- Support for databases like PostgreSQL, MySQL, and Redis when configured with proper backup and high availability.
For production databases, consider using Azure Database for PostgreSQL or Cosmos DB instead, but AKS is viable for custom stateful services.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Multi-Cluster and Hybrid Deployments with Azure Arc
Enterprises often need to manage clusters across environments. Azure Arc enables:
- Connecting on-premises, edge, and multi-cloud Kubernetes clusters to Azure.
- Applying consistent policies, security, and governance across all clusters.
- Deploying Azure services like Application Insights or Azure Monitor to non-Azure clusters.
This makes AKS part of a larger hybrid cloud strategy, not just a public cloud solution.
AI and Machine Learning Workloads on AKS
AKS is increasingly used for AI/ML workloads due to its scalability and GPU support:
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Deploy TensorFlow or PyTorch training jobs using GPU-enabled node pools.
- Scale inference endpoints with KFServing or Seldon Core.
- Integrate with Azure Machine Learning service for end-to-end MLOps.
Microsoft’s partnership with NVIDIA enhances AKS with optimized drivers and container images for AI workloads.
What is Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)?
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a managed Kubernetes service from Microsoft Azure that simplifies deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications. It handles the control plane management, allowing users to focus on application development.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
How much does AKS cost?
AKS itself is free—Microsoft does not charge for the control plane. You only pay for the underlying resources like VMs, storage, and networking. Optional services like monitoring or security may incur additional costs.
Can I run AKS on-premises?
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Not directly. AKS runs in Azure, but you can use Azure Arc to connect and manage on-premises Kubernetes clusters with AKS-like governance and tooling.
How do I secure my AKS cluster?
Secure AKS by enabling Azure AD integration, using managed identities, applying network policies, enabling Microsoft Defender for Containers, and following zero-trust principles with private clusters and minimal RBAC permissions.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What is the difference between AKS and Azure Container Instances (ACI)?
AKS is a full Kubernetes platform for orchestrating containers at scale, while ACI is a serverless container service for running single containers without managing infrastructure. ACI can be used with AKS via virtual nodes for burst scaling.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is more than just a managed Kubernetes offering—it’s a powerful platform that bridges development agility with enterprise-grade security, scalability, and integration. From setting up your first cluster to implementing advanced GitOps and AI workloads, AKS provides the tools and flexibility needed to modernize applications in the cloud. By leveraging automation, security best practices, and cost optimization strategies, organizations can unlock the full potential of containerization while maintaining control and compliance. Whether you’re a startup or a global enterprise, AKS empowers you to innovate faster, scale smarter, and operate more securely in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: