Azure SQL Database: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know in 2024
If you’re building modern cloud applications, Azure SQL Database is a game-changer. This fully managed relational database service from Microsoft delivers high performance, scalability, and security—all with minimal administrative effort.
What Is Azure SQL Database?

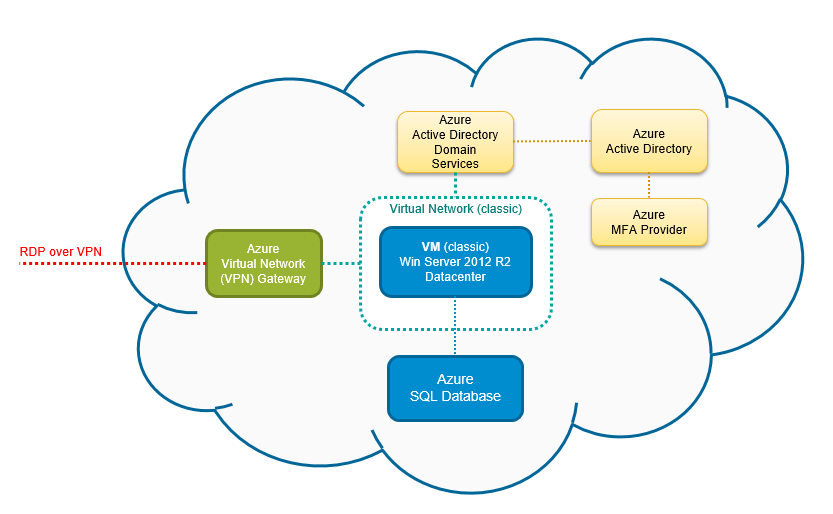
Azure SQL Database is Microsoft’s intelligent, fully managed relational cloud database service built on the Microsoft SQL Server engine. It’s designed to power modern applications with built-in intelligence, scalability, and security. As a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering, it removes the need for infrastructure management, letting developers and IT teams focus on innovation rather than maintenance.
Core Architecture and Design
The foundation of Azure SQL Database lies in its cloud-native architecture. Unlike traditional on-premises SQL Server deployments, it runs on Microsoft Azure’s global infrastructure, ensuring high availability and disaster recovery by default. The service uses a control plane and data plane separation, enabling automated patching, backups, and failover without user intervention.
- Runs on the latest stable version of SQL Server Database Engine
- Leverages hyper-scale compute and storage resources
- Supports multi-tenant and single-tenant deployment models
One of the key differentiators is its ability to automatically tune and optimize query performance using AI-driven insights. This built-in intelligence helps reduce manual tuning efforts and improves application responsiveness over time.
Differences Between Azure SQL Database and SQL Server
While both share the same core engine, Azure SQL Database and SQL Server serve different use cases. SQL Server is typically deployed on-premises or in virtual machines, requiring full management of the operating system, updates, and high availability configurations.
- Azure SQL Database is fully managed; SQL Server requires manual administration
- SQL Database scales automatically; SQL Server scaling requires planning and intervention
- SQL Database offers built-in geo-replication; SQL Server needs complex configuration for DR
According to Microsoft’s official documentation, Azure SQL Database is optimized for SaaS applications, microservices, and cloud-native development, making it ideal for organizations undergoing digital transformation.
“Azure SQL Database allows developers to focus on building apps, not managing databases.” — Microsoft Azure Team
Key Benefits of Using Azure SQL Database
Organizations choose Azure SQL Database not just for its technical capabilities but for the tangible business value it delivers. From cost savings to faster time-to-market, the benefits are substantial and measurable.
Automatic High Availability and Disaster Recovery
One of the most compelling advantages is built-in high availability. Azure SQL Database guarantees 99.99% availability for business-critical tiers through a combination of zone-redundant replicas and automatic failover.
- Zone-redundant deployments span multiple availability zones
- Automatic failover within seconds during outages
- Point-in-time restore up to 35 days (longer with advanced options)
This level of resilience is difficult and expensive to achieve with on-premises systems. For example, a financial services company using Azure SQL Database reported zero downtime during a regional Azure outage due to geo-failover capabilities.
Intelligent Performance Optimization
Azure SQL Database uses machine learning to continuously monitor and improve query performance. Features like Automatic Tuning can identify inefficient queries and suggest or apply fixes automatically.
- Identifies missing indexes and creates them
- Forces optimal execution plans to prevent performance regressions
- Provides performance recommendations via the Azure portal
A retail company saw a 40% improvement in query response times after enabling Automatic Tuning, without any code changes. This kind of self-optimizing behavior is a hallmark of modern cloud databases.
Deployment Models and Service Tiers
Azure SQL Database offers flexible deployment options tailored to different workload requirements. Choosing the right model and tier is crucial for balancing performance, cost, and scalability.
Single Database vs. Elastic Pool
The two primary deployment models are Single Database and Elastic Pool. A Single Database is ideal for applications with predictable, isolated workloads. It operates independently with dedicated resources.
- Best for mission-critical applications needing guaranteed performance
- Easy to manage and monitor individually
- Supports all advanced features like Hyperscale and serverless
An Elastic Pool, on the other hand, allows multiple databases to share a pool of resources (CPU, memory, IOPS). This is perfect for SaaS providers managing hundreds of customer databases with varying usage patterns.
- Cost-effective for variable or unpredictable workloads
- Enables resource sharing while maintaining isolation
- Automatically balances load across databases
For instance, a healthcare SaaS platform reduced its database costs by 60% by switching from individual databases to an elastic pool, where peak usage was spread across different time zones.
Service Tiers: DTU vs. vCore
Azure SQL Database offers two purchasing models: DTU (Database Transaction Unit) and vCore (virtual Core). The DTU model is a bundled metric combining CPU, memory, and I/O into a single unit, making it simple for beginners.
- DTU model: Simple, fixed tiers (Basic, Standard, Premium)
- Best for small to medium apps with stable workloads
- Limited flexibility in resource customization
The vCore model provides granular control over compute, storage, and licensing. It supports both provisioned and serverless compute, making it ideal for enterprises with complex requirements.
- vCore model: Full transparency into resource usage
- Supports SQL Server license benefits (BYOL)
- Enables advanced scenarios like Hyperscale and business continuity
According to a Microsoft pricing guide, the vCore model often provides better cost efficiency for large-scale deployments.
Scalability and Performance Options
Scalability is at the heart of Azure SQL Database’s design. Whether you need to handle sudden traffic spikes or plan for long-term growth, the platform adapts seamlessly.
Vertical and Horizontal Scaling Capabilities
Vertical scaling (scaling up/down) is straightforward—simply change the service tier or vCore count. This can be done with near-zero downtime, often in under a minute.
- Scale compute independently of storage in vCore model
- Automate scaling using Azure Monitor alerts and PowerShell scripts
- Supports up to 100 TB of storage in Hyperscale tier
Horizontal scaling is achieved through sharding or using Elastic Query to distribute data across multiple databases. While not automatic, Azure provides tools like Elastic Database Tools to simplify sharding logic in applications.
“With Azure SQL Database, scaling isn’t a weekend project—it’s a button click.” — Cloud Architect, Tech Innovations Inc.
Hyperscale and Serverless Options
The Hyperscale service tier is designed for large-scale applications requiring rapid scaling and high throughput. It decouples compute from storage, allowing databases to grow up to 100 TB with minimal performance impact.
- Enables read-scale out with up to 4 replicas
- Fast scaling and cloning for dev/test environments
- Ideal for data-intensive apps like analytics platforms
The Serverless compute tier is perfect for intermittent or unpredictable workloads. It automatically pauses the database during inactivity and resumes when needed, significantly reducing costs.
- Pays only when the database is active
- Auto-pause after a configurable idle period (e.g., 1 hour)
- Ideal for development, testing, and low-traffic production apps
A startup using serverless reported a 70% reduction in monthly database costs compared to a always-on provisioned model.
Security and Compliance Features
In today’s regulatory landscape, data security isn’t optional—it’s essential. Azure SQL Database provides a comprehensive suite of security features to protect sensitive information.
Data Encryption and Access Control
All data in Azure SQL Database is encrypted at rest by default using Transparent Data Encryption (TDE). This ensures that even if physical storage is compromised, the data remains secure.
- TDE uses AES-256 encryption
- Customer-managed keys supported via Azure Key Vault
- Encryption in transit enforced via TLS
Access control is managed through Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) integration, enabling centralized identity management. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and conditional access policies further strengthen security.
- Supports Azure AD authentication for users and applications
- Role-based access control (RBAC) for granular permissions
- Integration with Microsoft Entra ID for zero-trust security models
A government agency using Azure SQL Database achieved compliance with FedRAMP and CJIS requirements by leveraging these built-in encryption and identity features.
Threat Detection and Vulnerability Assessment
Azure SQL Database includes Advanced Data Security, a unified package that includes threat detection, vulnerability assessment, and data discovery & classification.
- SQL Injection and anomalous query detection
- Real-time alerts sent to Azure Security Center
- Automated vulnerability scans with remediation guidance
For example, a financial institution detected a brute-force attack attempt through threat detection alerts and blocked the IP address before any data was accessed.
“Security in Azure SQL Database is proactive, not reactive.” — CISO, Global Bank Corp
Integration with Azure Ecosystem
One of Azure SQL Database’s greatest strengths is its seamless integration with other Azure services, enabling end-to-end cloud solutions.
Connecting with Azure App Services and Functions
Developers can easily connect Azure SQL Database to web apps hosted on Azure App Service. Connection strings are securely stored in application settings, and integration with managed identities eliminates the need for hardcoded credentials.
- Managed identities enable passwordless database access
- Auto-healing and load balancing in App Service improve reliability
- CI/CD pipelines via Azure DevOps streamline deployments
Similarly, Azure Functions can trigger database operations based on events (e.g., file uploads, API calls), enabling serverless data processing workflows.
Data Integration with Azure Synapse and Power BI
For analytics, Azure SQL Database integrates smoothly with Azure Synapse Analytics. You can offload reporting workloads to Synapse without impacting transactional performance.
- Use PolyBase to query data directly from SQL Database
- Replicate data via Azure Data Factory or Log Replay Service
- Enable real-time analytics with minimal latency
Business intelligence teams often connect Azure SQL Database to Power BI for interactive dashboards. DirectQuery mode allows live data visualization without data duplication.
A marketing analytics firm reduced report generation time from hours to minutes by connecting Power BI directly to their Azure SQL Database instance.
Migration Strategies to Azure SQL Database
Migrating from on-premises or other cloud databases to Azure SQL Database requires careful planning. Microsoft provides several tools to simplify the process.
Using Azure Database Migration Service (DMS)
Azure Database Migration Service (DMS) is a fully managed service that supports online (zero-downtime) migrations from SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and other sources.
- Assesses on-premises databases for compatibility issues
- Performs schema and data migration with minimal downtime
- Supports continuous data synchronization during cutover
A manufacturing company successfully migrated 50+ SQL Server databases to Azure SQL Database using DMS, completing the project over a weekend with no business disruption.
Hybrid Scenarios with Azure SQL Managed Instance
For organizations not ready to fully move to the cloud, Azure SQL Managed Instance offers a middle ground. It provides near 100% compatibility with on-premises SQL Server, including support for SQL Agent, cross-database queries, and CLR.
- Enables lift-and-shift migrations with minimal changes
- Supports VNet integration and private endpoints
- Acts as a stepping stone to Azure SQL Database
According to Microsoft, migration guides recommend starting with a pilot migration using DMS and Managed Instance before transitioning to Azure SQL Database for new applications.
Monitoring, Management, and Automation
Effective database management doesn’t end with deployment. Continuous monitoring and automation are key to maintaining performance and reliability.
Using Azure Monitor and Query Performance Insights
Azure Monitor collects metrics, logs, and alerts for Azure SQL Database. You can track CPU usage, DTU percentage, deadlocks, and more in real time.
- Create custom dashboards for database health
- Set up alerts for performance thresholds
- Export logs to Log Analytics or Event Hubs
Query Performance Insights helps identify the most resource-intensive queries and their historical impact. It provides a visual breakdown of CPU, I/O, and memory consumption per query.
“Performance insights turned our reactive DBA team into proactive optimizers.” — IT Manager, E-Commerce Co.
Automation with PowerShell and Azure CLI
Administrative tasks like scaling, backups, and user management can be automated using PowerShell or Azure CLI scripts.
- Scale databases based on time or load triggers
- Automate backup retention policies
- Deploy databases using Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) templates
A DevOps team automated nightly scaling down of non-production databases, saving over $15,000 annually in cloud costs.
What is Azure SQL Database?
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed relational database service in the cloud, built on the SQL Server engine. It offers high availability, intelligent performance, and built-in security, making it ideal for modern cloud applications.
How much does Azure SQL Database cost?
Pricing depends on the service tier (DTU or vCore), compute size, storage, and features. Costs can range from a few dollars per month for serverless databases to thousands for large Hyperscale deployments. Use the Azure Pricing Calculator for accurate estimates.
Can I migrate my on-prem SQL Server to Azure SQL Database?
Yes, you can migrate using tools like Azure Database Migration Service (DMS). However, some features (e.g., SQL Agent, cross-database queries) are not supported. For full compatibility, consider Azure SQL Managed Instance as an intermediate step.
Is Azure SQL Database secure?
Yes, it includes robust security features like Transparent Data Encryption, Azure AD authentication, threat detection, and vulnerability assessment. It’s compliant with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
What is the difference between Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance?
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed PaaS with limited on-premises feature parity, while Azure SQL Managed Instance offers near-complete SQL Server compatibility and is ideal for lift-and-shift migrations.
In conclusion, Azure SQL Database is more than just a cloud version of SQL Server—it’s a powerful, intelligent database platform designed for the modern era. With its automated management, scalability, security, and deep integration into the Azure ecosystem, it empowers organizations to build resilient, high-performance applications with less overhead. Whether you’re a startup or an enterprise, adopting Azure SQL Database can accelerate your cloud journey and deliver real business value.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: